
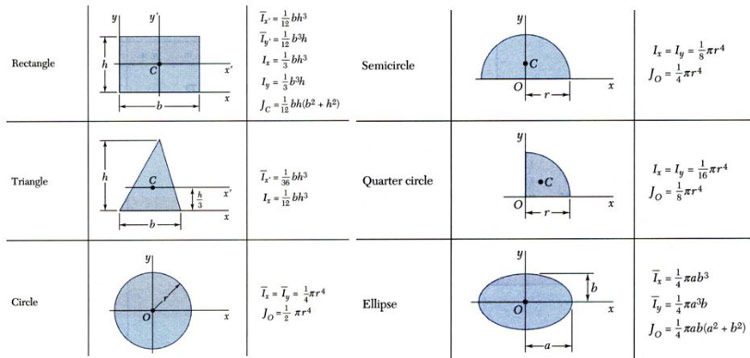
Thus, the moment of inertia of the shaded region is less about the y-axis as compared to x-axis.ĭetermine the moment of inertia of y = 2 - 2x 2 about the x axis. The area is more closely distributed about the y-axis than x-axis. The next integration along the x direction goes from 0 to 4. Thus the limits of integration is 0 to y. The diagram at the left shows the dy going from 0 to the curve, or just y.

Again, the integration will be done first along the y direction, and then along the x direction. The integral is still split into integration along the x direction (dx) and along the y direction (dy). But in this case, it is about the y-axis, or Similar to the previous solution is part a), the moment of inertia is the second moment of the area about a given axis or line. The final integration from isĮxpanding the bracket by using the formula, This order is easier since the curve function is given as y is equal to a function of x. The order of integration, dx or dy, is optional, but usually there is an easy way, and a more difficult way.įor this problem, the integration will be done first along the y direction, and then along the x direction. This also requires the integral be split into integration along the x direction (dx) and along the y direction (dy).
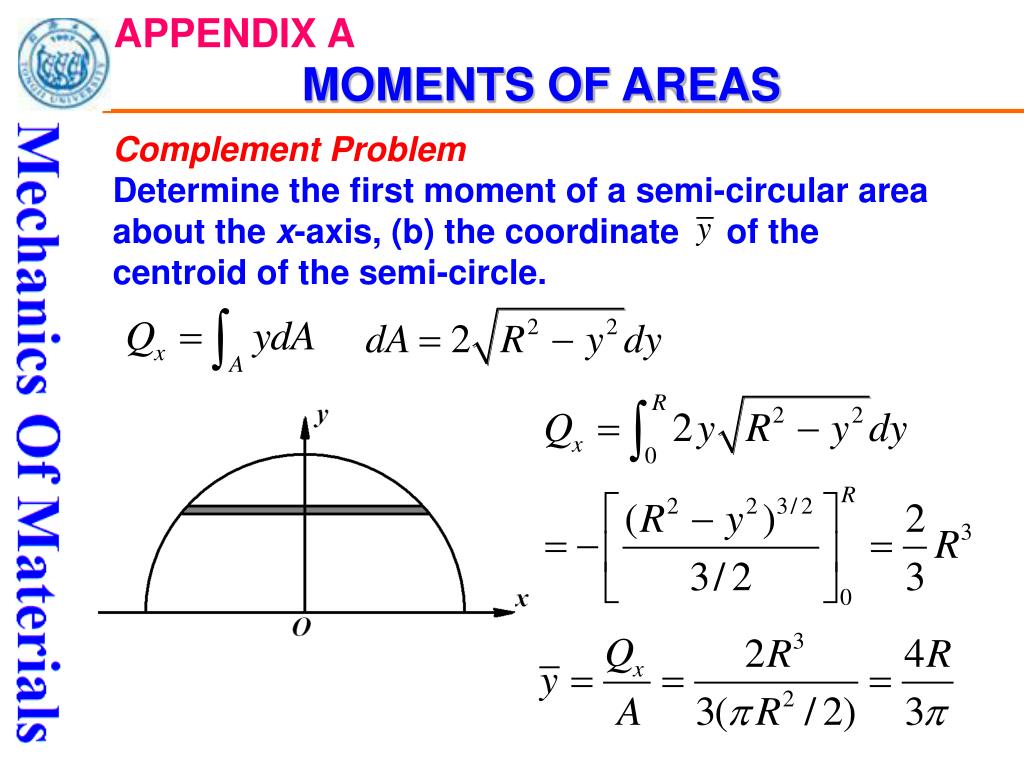
The differential element, dA, is usually broken into two parts, dx and dy (dA = dx dy), which makes integration easier. Recall, the moment of inertia is the second moment of the area about a given axis or line.įor part a) of this problem, the moment of inertia is about the x-axis. Find moment of inertia of the shaded area about


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
